I recently wanted to debug a Rust program on Windows that I had written, and was struggling with how to get it to work. Since there was quite a lot of hoops to jump through to get it to work, I though I should share it with other people as well. I've written this blog post from memory and I'm far from an expert in LLVM or Rust, so if you see something strange here then let me know.
The drawback of this approach is that you can't debug applications built using the MSVC toolchain. If you know how to do this, please tell me. I would really appreciate it.
UPDATE 2018-02-02:
As Stuart Dootson pointed out to me, there's a guide on how to debug applications using the MSVC toolchain here. I haven't tried this out myself, but it looks promising. Thanks Stuart!
1. Install LLVM
First we need to install LLVM which is a compiler infrastructure. Part of LLVM is LLDB which is the debugger we're going to use. The latest version of LLVM doesn't include Python support for LLDB which is required for the VSCode extension, so we need to download a custom built version and install that.
https://github.com/vadimcn/llvm/releases
2. Install Python
We now need to install Python v3.5 (Not v3.6).
https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-354/
If you installed the x64 version of LLVM, make sure that you install the x64 version of Python as well, otherwise you will encounter problems later on.
3. Make sure it works
Make sure that lldb can use scripting. If this doesn't work, make sure that both LLVM and Python is on PATH.
C:> lldb
(lldb) script
Python Interactive Interpreter. To exit, type 'quit()', 'exit()' or Ctrl-D.
Write exit() to close the Python interpreter and then CTRL+C to break out of LLDB.
4. Install the VSCode extension
We now need to install the vscode-lldb extension for Visual Studio Code. This is what makes it possible to debug our Rust code from Visual Studio Code.
https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=vadimcn.vscode-lldb
5. Install the Rust GNU toolchain
Since LLDB doesn't work with the msvc compiler, we need to install the Rust GNU toolschain and use that one. This have some drawbacks though such as we won't be able to intop with software produced by Visual Studio.
C:> rustup install stable-gnu
6. Set the active toolchain
We now need to set the Rust GNU toolchain as the active toolchain. We do this by using the rustup command again.
C:> rustup default stable-gnu
We should now verify what our toolchain configuration look like by using rustup show.
C:> rustup show
Default host: x86_64-pc-windows-msvc
installed toolchains
--------------------
stable-x86_64-pc-windows-gnu (default)
stable-x86_64-pc-windows-msvc
beta-x86_64-pc-windows-msvc
nightly-2017-12-08-x86_64-pc-windows-msvc
nightly-x86_64-pc-windows-msvc
active toolchain
----------------
stable-x86_64-pc-windows-gnu (default)
rustc 1.23.0 (766bd11c8 2018-01-01)
7. Create a project
Create a new project called hello_world.
C:\Source> cargo new --bin hello_world
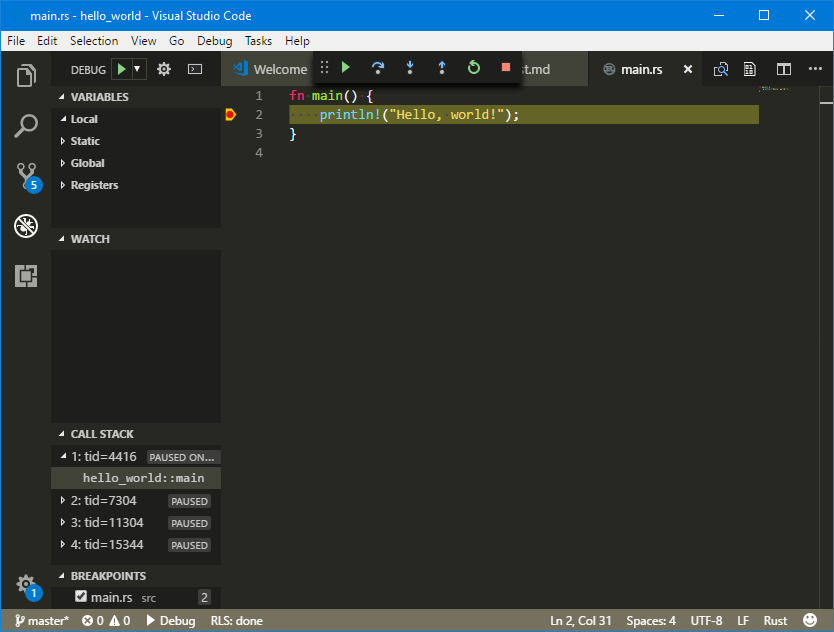
Open Visual Studio Code and go to ./src/main.rs and place a breakpoint.
8. Edit launch.json
Press F5 to run the project. A selection box will appear that will ask you what environment you want to use. Choose LLDB Debugger here. This will open up the launch.json file, and here we need to tell Visual Studio Code how to launch our project. Edit the file so it looks similar to this:
{
// Use IntelliSense to learn about possible attributes.
// Hover to view descriptions of existing attributes.
// For more information, visit: https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?linkid=830387
"version": "0.2.0",
"configurations": [
{
"type": "lldb",
"request": "launch",
"name": "Debug",
"program": "${workspaceRoot}/target/debug/hello_world",
"args": [],
"cwd": "${workspaceRoot}/target/debug/"
}
]
}
9. Profit
Press F5 again. You should now be debugging your code.